A key player in this effort is NeuronBank, an innovative tool that centralizes and organizes vast amounts of neuron-related data. This article explores the contribution of NeuronBank in advancing research into neurodegenerative diseases, helping scientists uncover new insights and develop more effective treatments.
Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s disease affect millions of people worldwide, leading to debilitating conditions that significantly impact quality of life. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of these diseases is one of the most pressing challenges in modern neuroscience.
A powerful resource for understanding neural degeneration
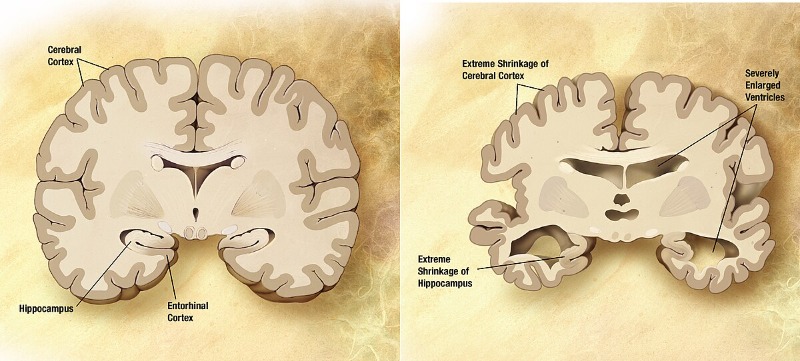
Neurodegenerative diseases are characterized by the progressive loss of neuron function and structure, leading to cognitive decline, motor dysfunction, and other severe symptoms. These conditions often involve the death of specific neurons in the brain, which disrupts neural circuits and affects the entire nervous system. Understanding which neurons are involved and how their degeneration progresses is crucial for developing targeted therapies.
The contribution of NeuronBank in this area is invaluable. By offering a centralized platform where researchers can catalog and analyze neuron data, NeuronBank enables scientists to identify patterns in neuron degeneration across different diseases. It allows researchers to cross-reference healthy neural circuits with those affected by neurodegenerative diseases, providing key insights into how and why certain neurons are more vulnerable than others.
NeuronBank’s ability to store detailed information on neuron types, synaptic connections, and molecular profiles helps researchers pinpoint the exact neural circuits that are impacted in neurodegenerative diseases. This comprehensive approach not only aids in understanding the progression of these diseases but also highlights potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
Mapping neural circuits in neurodegenerative diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases often affect specific neural circuits in the brain, leading to distinct symptoms such as memory loss in Alzheimer’s disease or motor dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Mapping these neural circuits is essential for understanding how these diseases disrupt normal brain function and for identifying potential points of intervention.
One of NeuronBank’s contributions is its ability to facilitate the mapping of neural circuits affected by neurodegenerative diseases. By compiling data from various studies and species, NeuronBank provides researchers with a detailed view of how neurons are connected and how these connections change as a disease progresses.
For instance, in Alzheimer’s disease, the hippocampus — a region critical for memory — is one of the first areas to be affected. NeuronBank’s comprehensive database allows researchers to explore the specific neural circuits within the hippocampus and compare them with those in a healthy brain. This comparison helps scientists identify which neurons are most susceptible to the disease and how the breakdown of these circuits leads to cognitive decline.
Similarly, in Parkinson’s disease, motor control is affected by the degeneration of neurons in the substantia nigra, a region of the brain that produces dopamine. NeuronBank’s extensive neuron catalog enables researchers to study the exact circuits involved in motor function and understand how their disruption leads to the characteristic tremors and stiffness associated with Parkinson’s disease. This level of detail is crucial for developing treatments that target the specific neural circuits impacted by these diseases.
Facilitating cross-species comparisons in disease research
Neurodegenerative diseases are not confined to humans; many animal models are used to study these conditions, including mice, fruit flies, and even certain types of fish. These models help researchers understand the genetic, molecular, and cellular mechanisms that underlie neurodegeneration. However, comparing neuron data across different species can be challenging due to variations in neuron types and brain structures.
NeuronBank’s contribution to facilitating cross-species comparisons is significant. The platform’s standardized framework for neuron classification allows researchers to compare neuron data across various species, ensuring that findings from animal models can be more easily translated into human research. This cross-species analysis is crucial for validating potential treatments and understanding the broader principles of neurodegeneration.
For example, in research on Huntington’s disease, which involves the progressive degeneration of neurons in the basal ganglia, scientists often rely on mouse models to study the disease’s progression. NeuronBank allows researchers to compare the neural circuits in these models with those in humans, helping to identify common pathways that may be targeted by treatments. This cross-species approach enhances the relevance of animal research to human neurodegenerative diseases, accelerating the development of potential therapies.
Accelerating drug development for neurodegenerative diseases
Developing effective treatments for neurodegenerative diseases is a complex and time-consuming process. One of the main challenges is identifying which neurons and neural circuits should be targeted by drugs or other therapies. NeuronBank’s contribution to drug development is vital, as it helps researchers focus on the most affected neural circuits and develop therapies that specifically target these areas.
By providing detailed information on neuron degeneration and synaptic connections, NeuronBank allows researchers to identify key points where interventions could slow or halt the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. For instance, in Alzheimer’s disease, researchers can use NeuronBank to study how amyloid plaques and tau tangles disrupt neural circuits, helping them identify drugs that might protect neurons from this damage.
In Parkinson’s disease, where dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra are lost, NeuronBank provides a wealth of data on how these neurons interact with other parts of the brain. This information is crucial for developing drugs that either protect these neurons or compensate for their loss by enhancing the function of related circuits.
NeuronBank also facilitates the testing of new therapies by allowing researchers to simulate how a drug might affect specific neural circuits before moving to clinical trials. This preclinical testing is essential for identifying potential side effects and ensuring that treatments target the intended neural circuits.
Supporting personalized medicine for neurodegenerative diseases
As the field of medicine moves toward more personalized treatments, the ability to tailor therapies to an individual’s specific neural profile becomes increasingly important. Neurodegenerative diseases affect different people in different ways, and understanding the unique neural circuits involved in each case is crucial for developing effective, individualized treatments.
NeuronBank’s contribution to personalized medicine lies in its ability to provide detailed neuron data that can be used to tailor treatments to individual patients. By analyzing a patient’s specific neural circuits and comparing them to the extensive database of neuron information in NeuronBank, doctors can develop more targeted therapies that address the patient’s unique needs.
For example, in Parkinson’s disease, some patients may experience more severe motor symptoms, while others may have more cognitive decline. NeuronBank allows doctors to analyze the specific neural circuits affected in each patient and develop treatments that target those circuits. This personalized approach can improve the effectiveness of treatments and reduce the risk of side effects.
Conclusion
The contribution of NeuronBank to neurodegenerative disease research is profound. By providing a centralized platform for neuron data, mapping neural circuits, facilitating cross-species comparisons, and supporting drug development, NeuronBank is helping to unlock the mysteries of diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s. As the platform continues to grow, it will play an increasingly important role in advancing our understanding of neurodegenerative diseases and developing effective treatments.